[경영자를 위한 AI와 딥러닝] 중간고사 공부
[경영자를 위한 AI와 딥러닝] 중간고사 공부]
2주차
-
신경망
-
구조
- 700 ~ 1000억(100 BN)개 정도의 신경망 세포들
- 신경망 세포들 간의 연결 고리
- Dendrite
- Axon: 신경세포의 몸체 (soma)
- 포텐셜을 측정 (voltage) ; 포텐셜의 변화밖에 없음
- spiking
- bursting
- chattering (갈수록 freq 빨라짐)
- 포텐셜을 측정 (voltage) ; 포텐셜의 변화밖에 없음
- Synapse: 신경세포 간의 연결 (한쪽은 dendrite 한쪽은 axon)
- neuro transmitter가 이동
- electric potential을 통해 이동
- 불확실성이 많은 확률적 프로세스; non-linear
- connectionism; 연결주의; 모든 정보는 연결에 포함되어있다
- Neural Computation
- add/ subtract
- multiplication
- modification
-
Neural Computation을 구현하는 것이 Deep Learning
- 인공신경망 Artificial Neural Networks
- Supervised Learning
- Universal Function Approximator; 비선형적 관계까지 배울 수 있는 가능성
- layered structures, deep
- connectionism by alexander bain (2주차 강의 40분 쯤)
- Neural Learning (Hebbian Learning Rule) 44분쯤
- 인공신경망 Artificial Neural Networks
-
Soma에 붙어있는 dendrit로 input
- w as weight
- axon을 통해 전달 (긴다리)
- node가 역치를 기점으로 1 or 0 과 같은 signal 발생
Perceptron
- simplist neural network
- computational model of mcculloch-pitts neuron
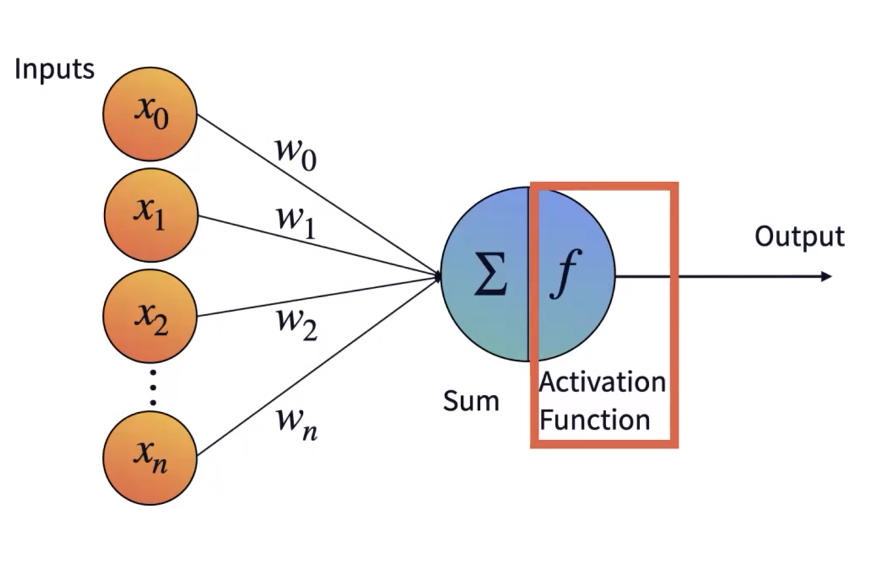
- activation function
- step (계단)
- sigmoid (S자)
- b as bias
- eventually $y=f(w*x)$
- AND/ OR Gate
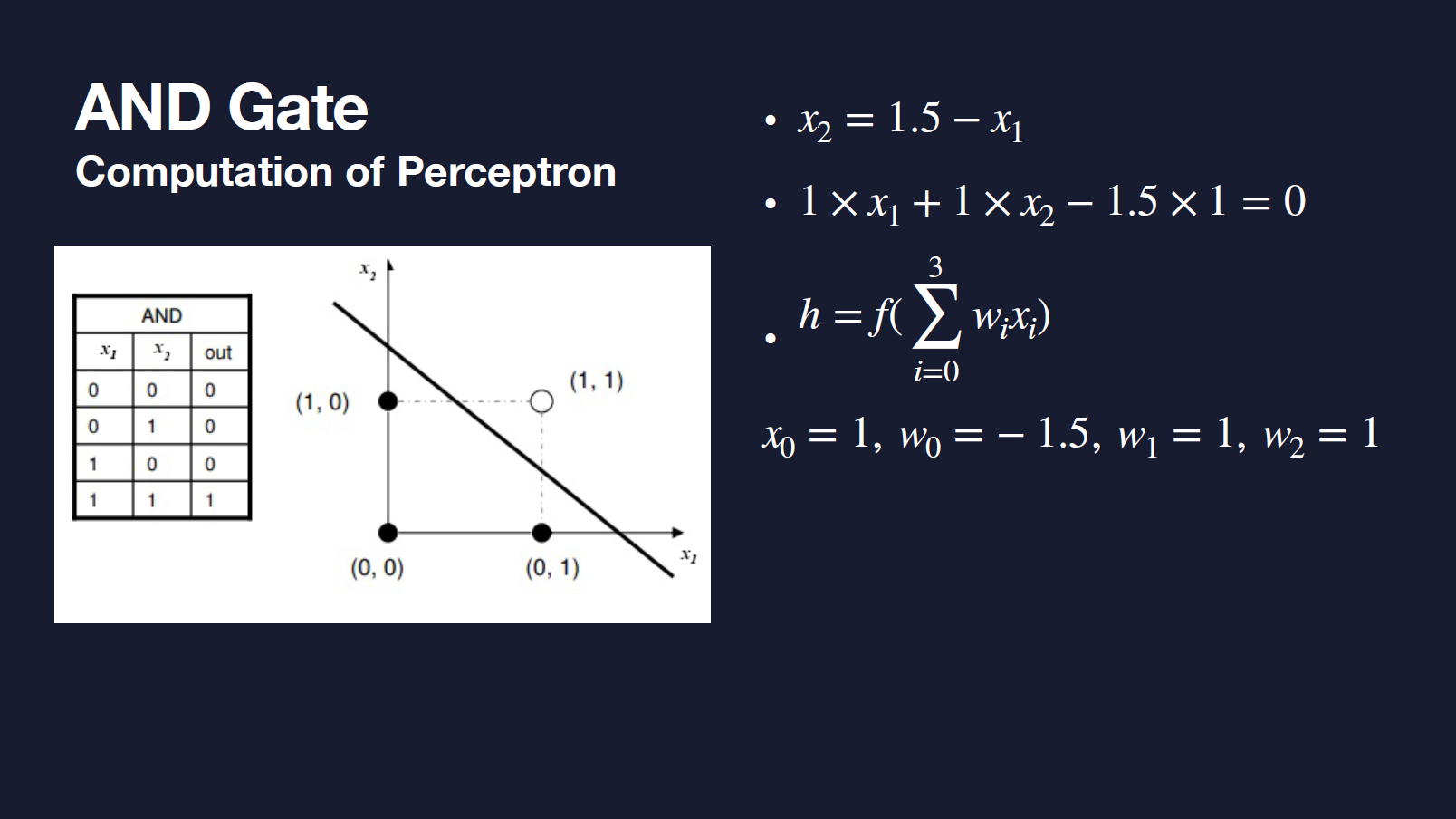
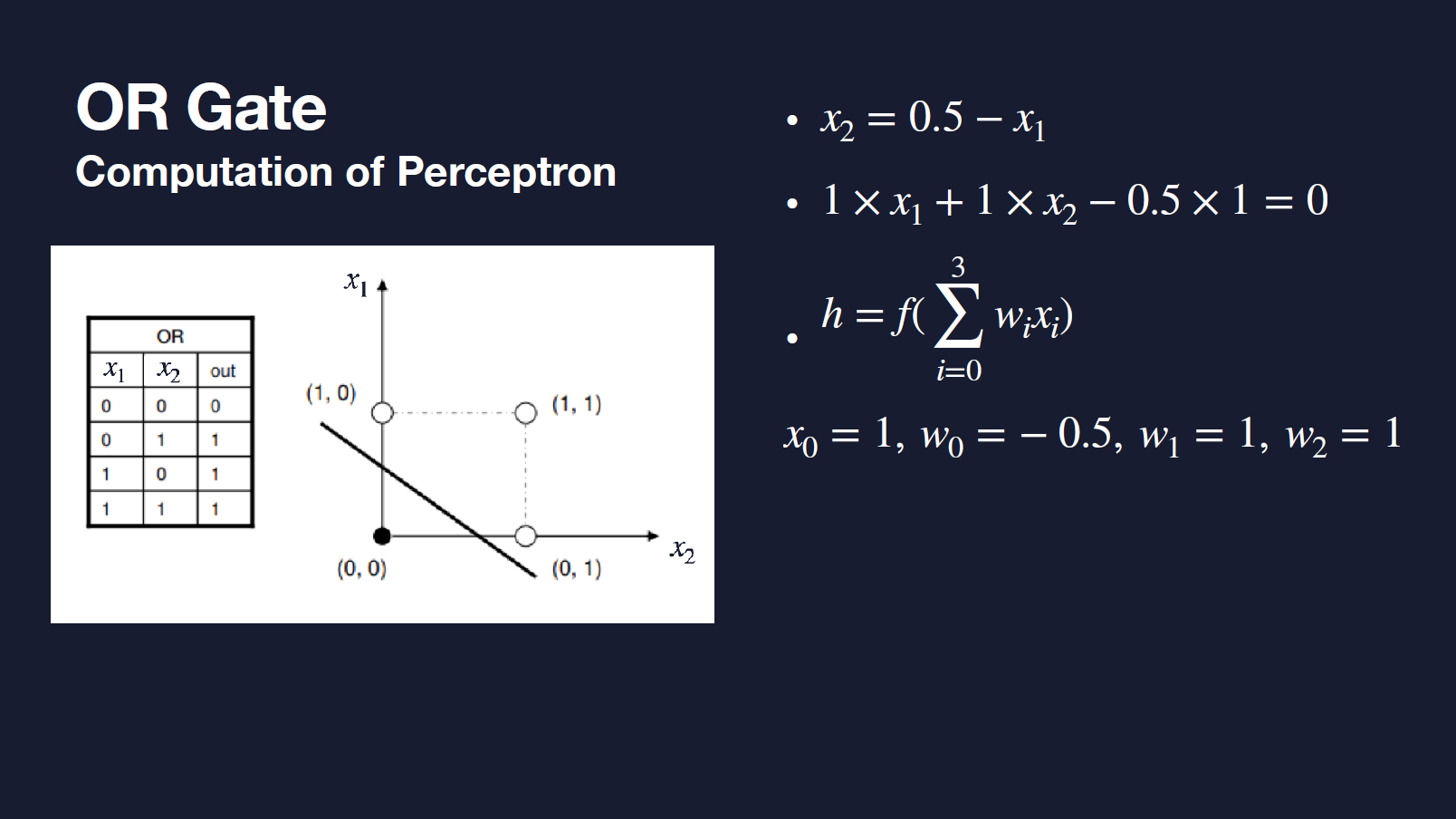
- XOR Gate https://youtu.be/Fg00LN30Ezg?t=385
- Perceptron Learning Rule

- a. initial learning model setting by setting w_i
- b. pick random x and check if the current learning model is right
- b-1. if $wx_1>0$, then do nothing, since it is right
- b-2. if $wx_2<0$, then w<-w+$\epsilon$; bit change to model
- c. keep going on until the end (satisfying all condition)
- Gradient Descent
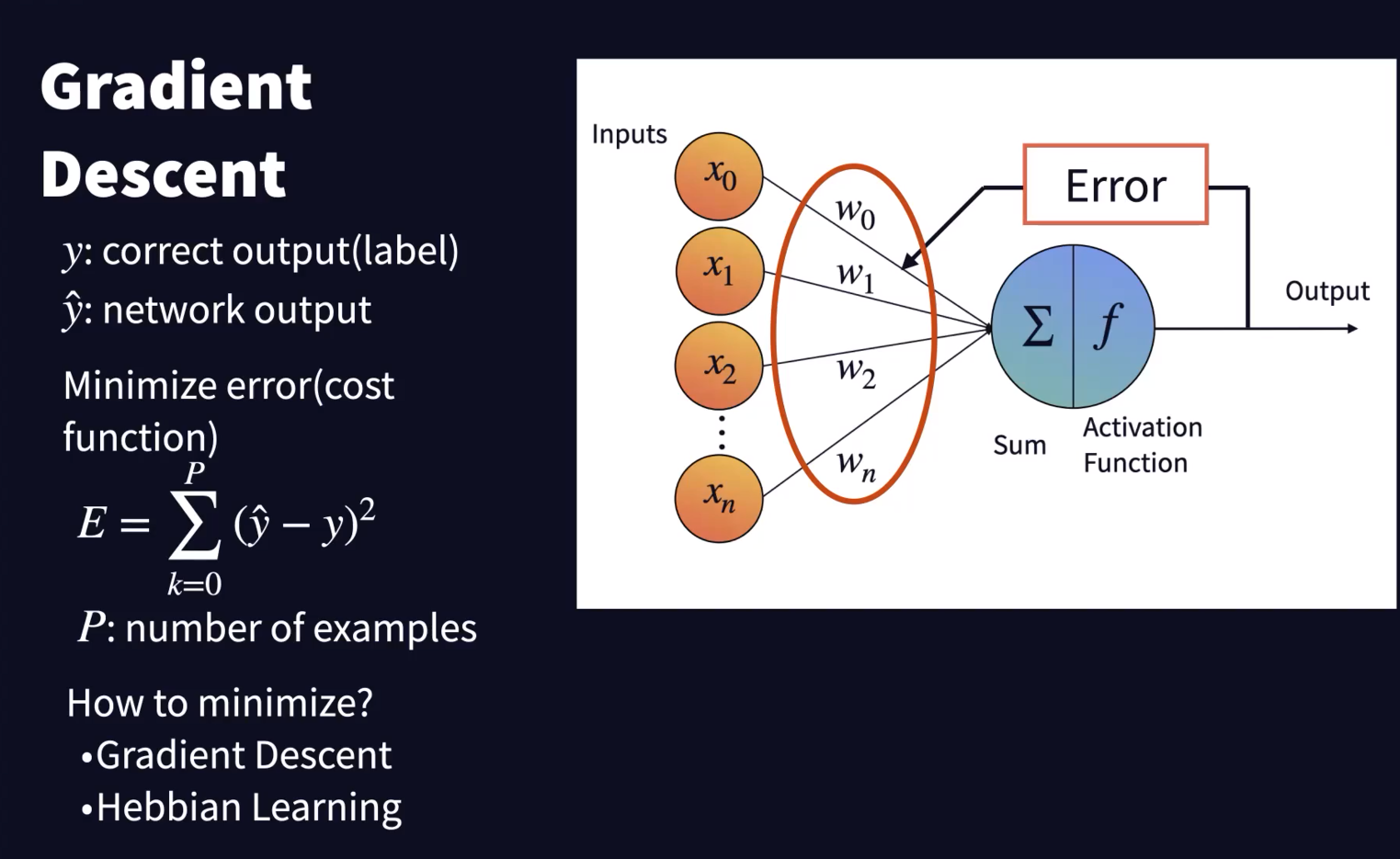
- control the weight movement under the logistics of minimizing (mean-squared) error
- Summary
- Perceptron is model for computation of a single neuron
- Hebbian learning rule can be derived from gradient-descent of the cost function.
3주차
- Coding
- Hellow to Tensorflow, Keras
4주차
-
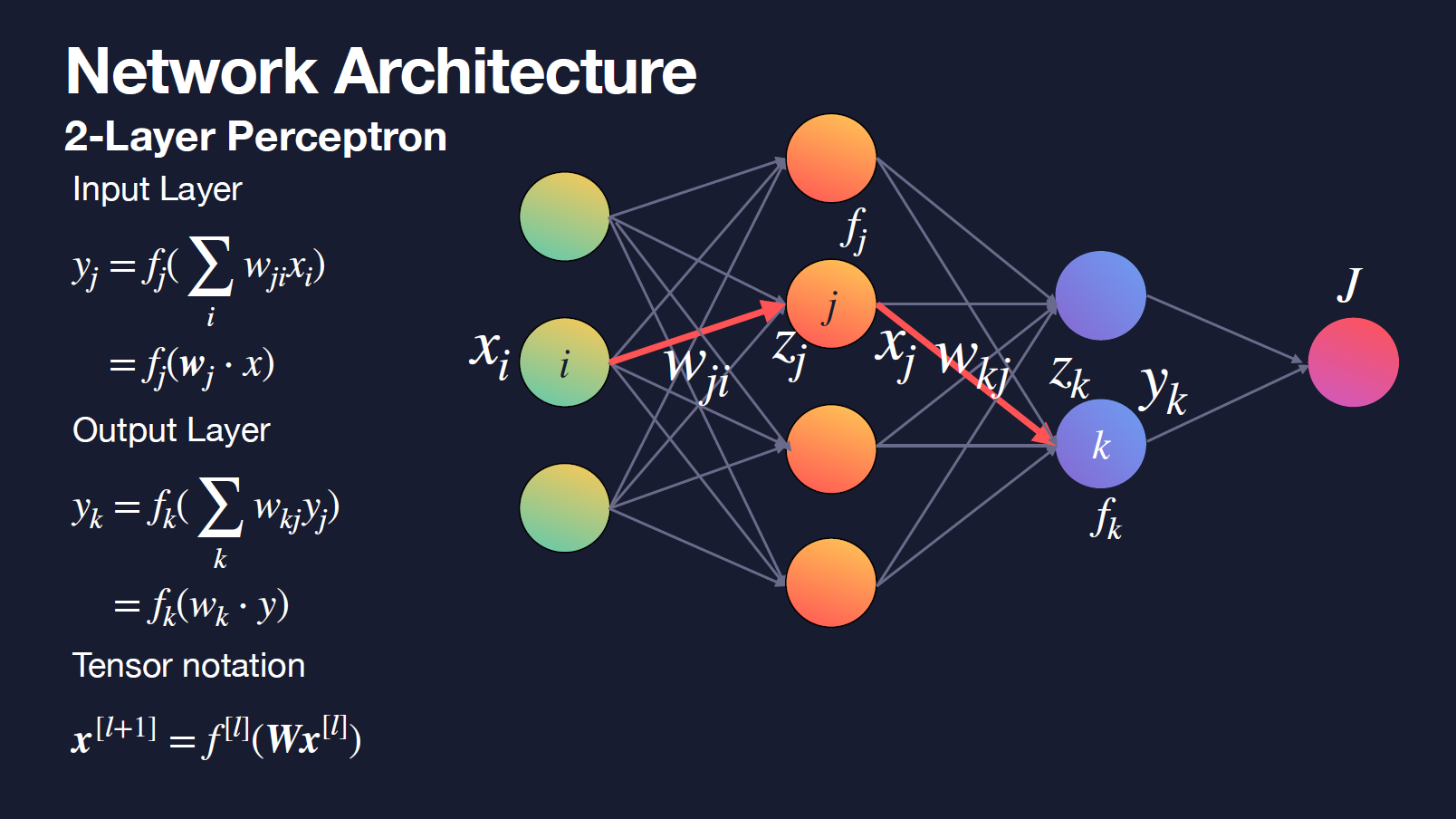
Tensor Notation for Neural Networks
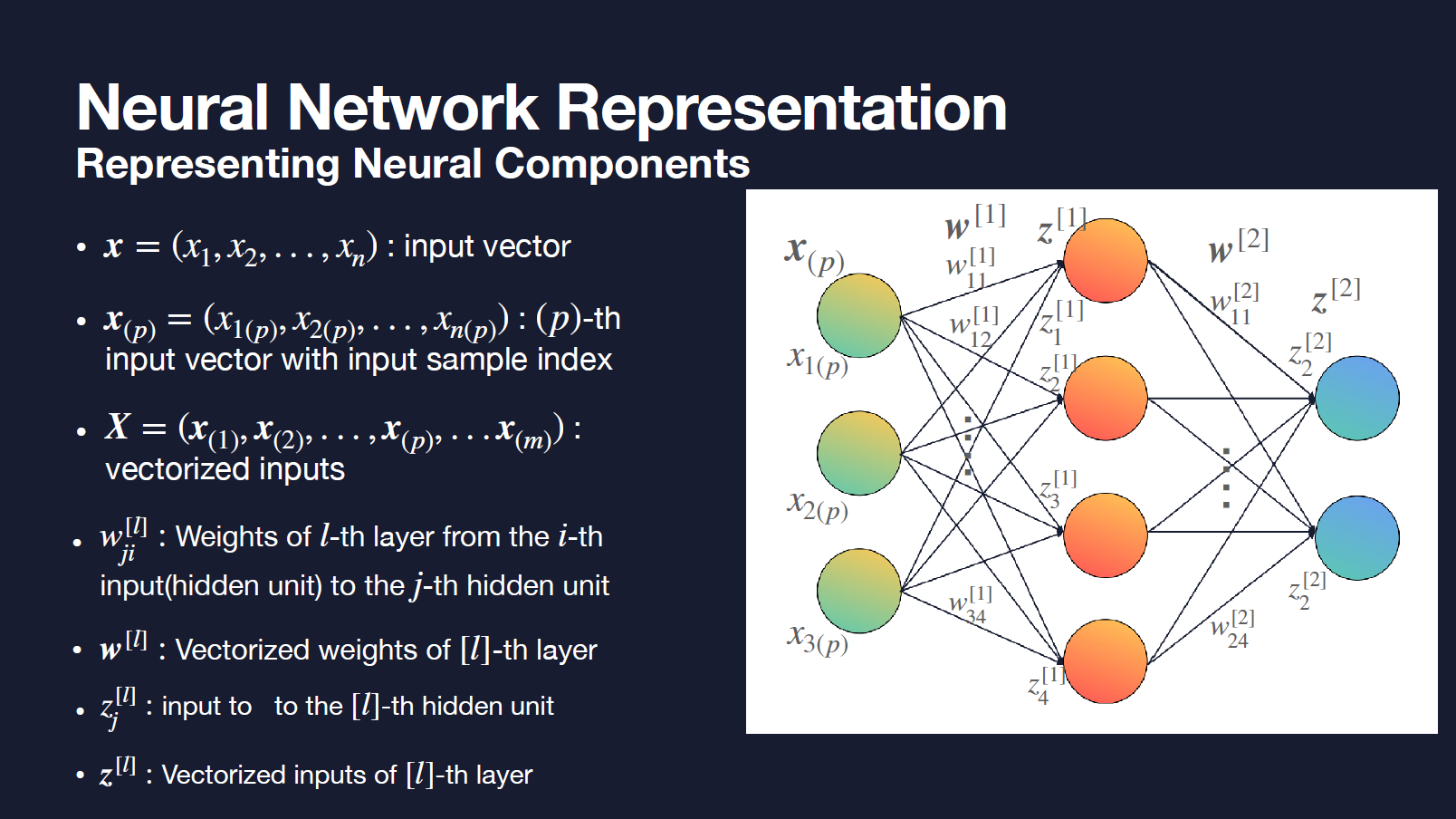
- input as x
- input vector as $x_{(p)}$
- $X=(x_{(1)},x_{(2)},x_{(3)}, …)$ as vectorized inputs
- $w_{ji}^{[l]}$ as weights of l-th layer from the i-th input to the j-th hidden unit
- node의 개수는 사용자가 선택하는 것이 아님, 이것을 만들어나가는 과정 자체가 딥러닝
- hidden layer, hidden node의 역할들 (구조들).. 블라블라
- TensorFlow
- Compute Tensors
- automatically compute the gradient of any differentiable tensors
- keras 라이브러리에 새로운 function이 contributed
- Tensorflow는 cpu, gpu,tpu 등을 전방위로 활용하여 matrix calculation 등을 진행 (기반)
- keras를 통해 텐서플로우 기반의 다양한 함수들 사용 가능
-
Matrix Multiplication
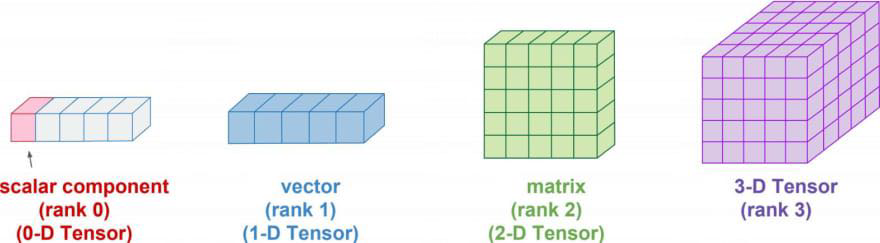
- Scalar
- rank 0 tensor (element of list(list is 1D; rank 1))
- Vector
- rank 1 tensor
- Numpy is a commonly used package for mathematical computation of list.
- Using Numpy we can compute vector and tensor effectively.
5주차
- Neural Network is Universal Function Approximator
- Understanding Tensor Representation for Deep Neural Networks
- X is tensorzied input
- 퍼셉트론으로 손글씨 인식 - Colaboratory (google.com)
6주차
- 디지털플랫폼 정부
- Multilayer Perceptron
- Training MLP using Back-propagation
- History: PDP Group
- Parallel Distributed Procesing
- Paul Werbos’ Backpropgation Algorithm (역전파)
- it’s all about adjusting weights
- Signals Propagate Forward
- input이 weight를 통해 hidden node를 거쳐 output으로 가는 forwarding
- Cost Function
- 실제 정답과 model로부터의 결과 간의 차이
- $J=(\hat\y-y)^2$
- Chain Rule : g’(x)f’(x)
- output node에 실제 정답(target output)을 기반으로 backpropagation을 통해 weight 조절
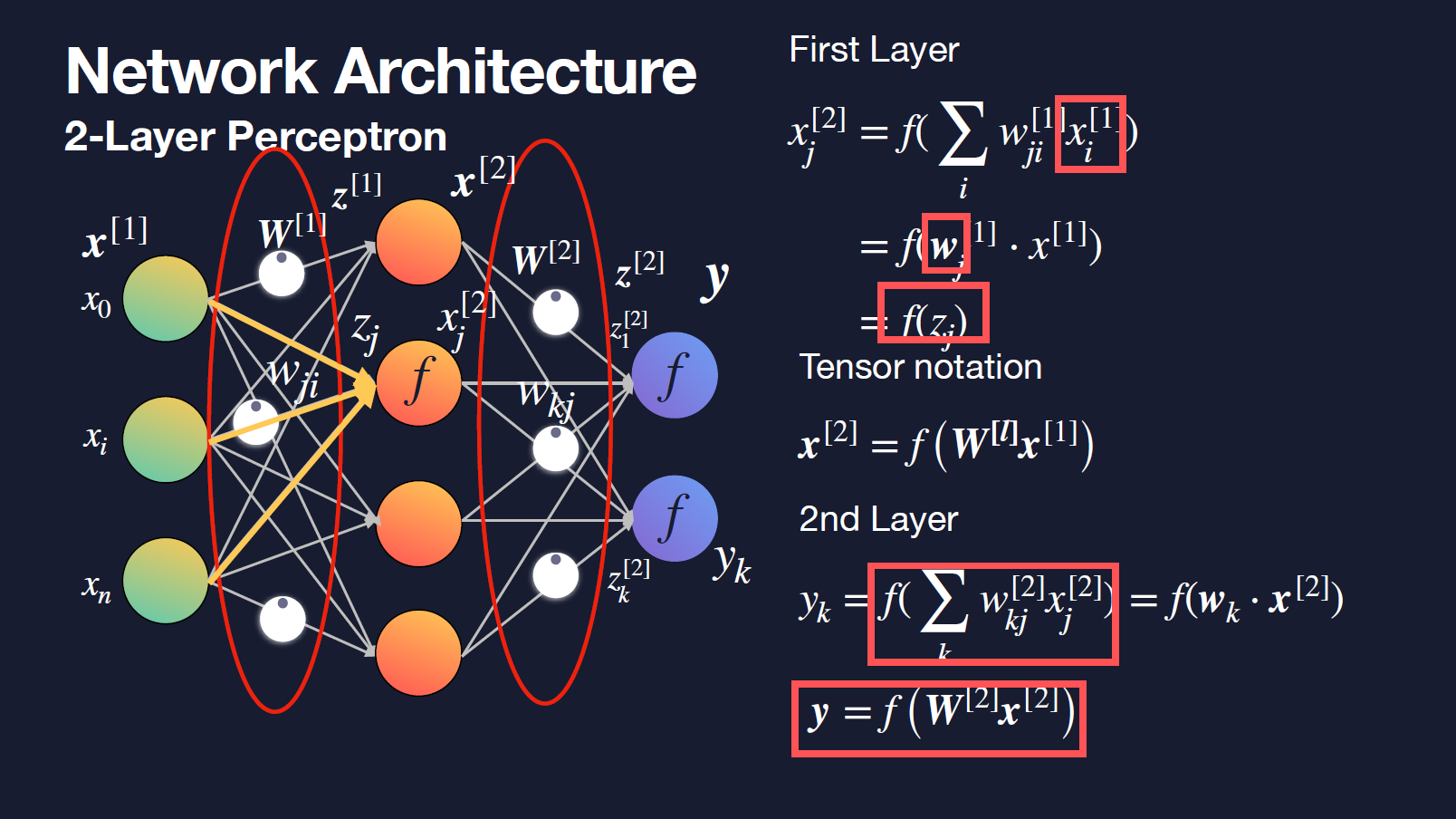
- always, it’s all about adjusting weight
- partial derivative (편미분)
- $w_{t+1} <- w_t -\gamma\Delta _wJ$
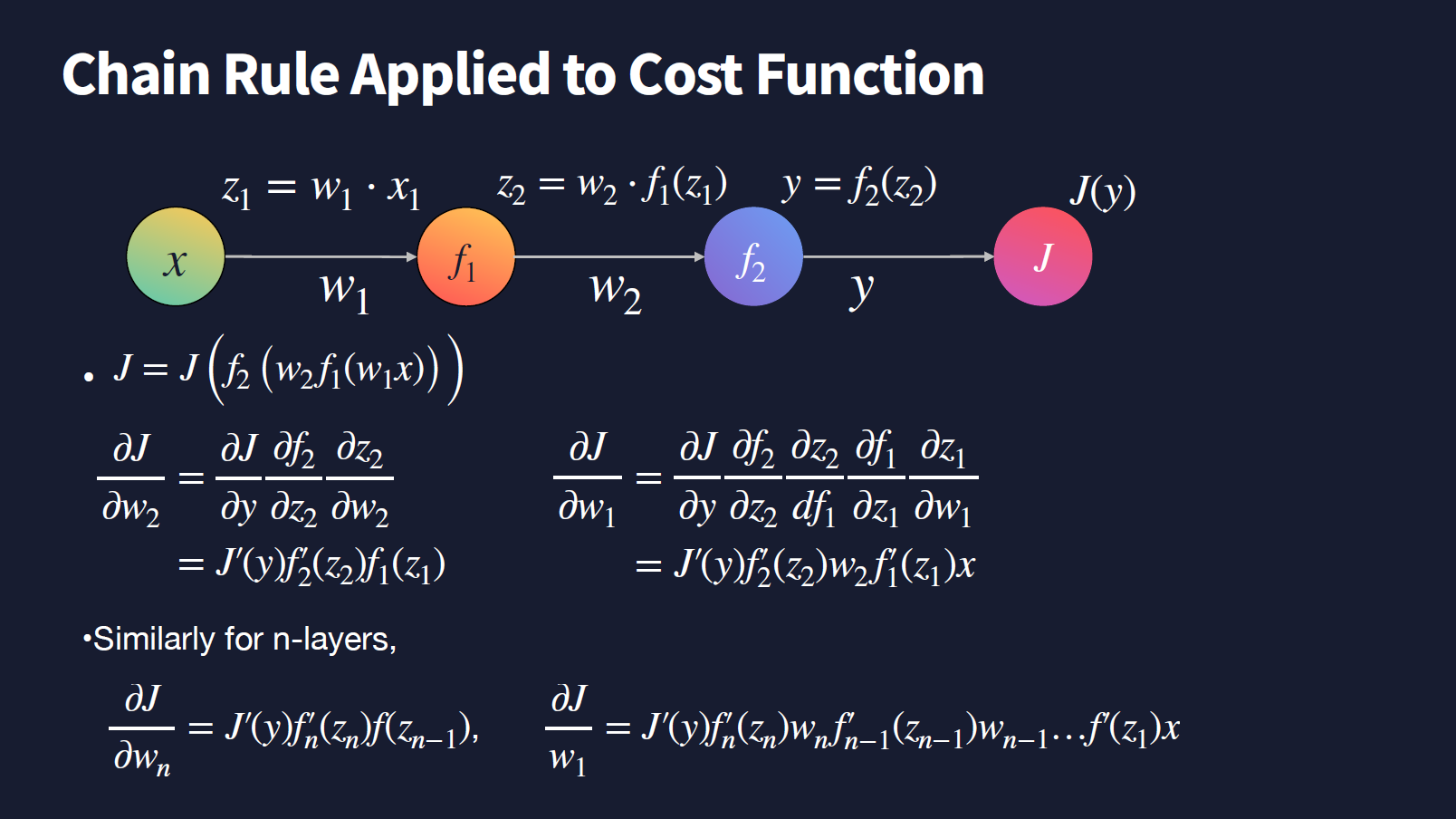
- layer 역순대로 미분 and so on
7주차
- Maximize Performance
- ML Workflow
- Gathering Data
- preprocess
- research the model
- train
- evaluate and update the model
- predict with satisfied model, otherwise? train again and again
- train and test
- hyperparameters: 알아서 다해요
- control the learning process
- topology and size of a neural network
- algorithm hyperparameters: learning rate, dropout rate, batch size
- control the learning process
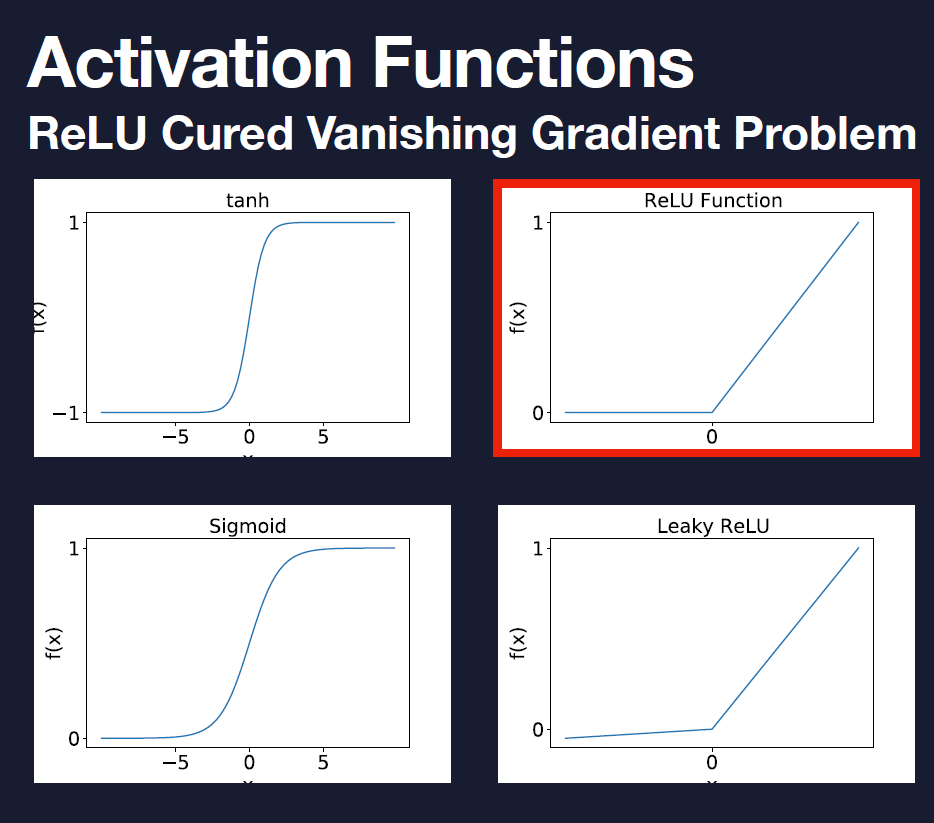
- Why ReLU?
- Sigmoid의 derivative 값이 작기 때문에 (대체로 .25 이하) 1보다 작은 값들을 계속 chain rule에 의해 곱하다보면 편미분값은 매우 작아지게 된다. 즉, vanishing
- asymptotic behavior
- ReLU는 derivative 값이 1 or 0뿐이므로 그 단점을 커버할 수 있음
- ML Workflow
- Various Implementatoin of Cost Function Optimization
- Batch
- loss function -> cost function을 minimize
- gradient 계산량이 많고, 시간이 많이 걸림
- Stochastic
- each new gradient’s loss function
- eventually approach to the optimal point
- Mini-Batch
- hybrid
- sample examples
- 두마리토끼, 계산량과 정확성
- Choosing
- small set<2000
- batch gradient
- large set
- mini batch of size 64~512
- small set<2000
- Batch
- local minima
- 쉬운게 없다
- or plateau
- multiple global minima
- depends on cost function, the minima can be differed
- Learning Rate
- parameters that control the learning process
- $\gamma$
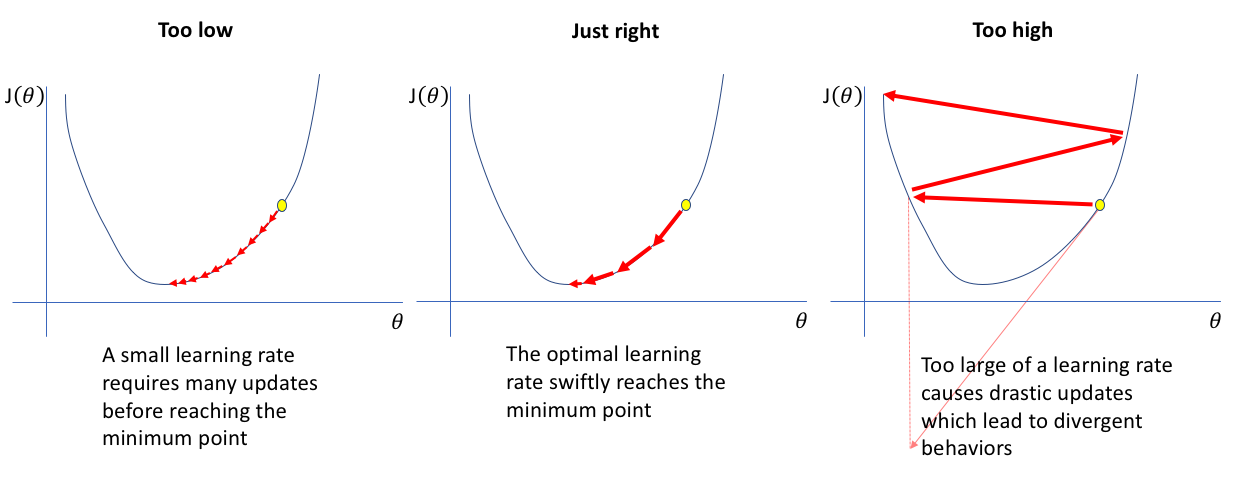
- Momentum
- for finding global minima
- 방향성에 대한 변수를 추가해 local minima에서만 머무르지 않도록
- Hyperparameter Tuning
- Monte-Carlo Search
- Optimizers
- Adam이 짱임 (최근으로선)
- Choice of Loss Function
- mean squared error
- regression or binary classification
- cross entropy
- multi class classification
- paired with the softmax actiavtion function
- mean squared error
- Under- and Over-fitting
- fix underfitting
- train longer
- increase the model complexity
- reducing regularizatoin
- adding features to trainig data
- different (appropriate) model or architecture
- fix overfitting
- adding more data
- data augmentation
- regularization
- decrease model complexity
- removing features from data
- early stopping
- balance between validatoin and error
- what is regularization?
- weight의 기울기를 급한 경사 안쪽으로
- Preprocessing
- normalization
- data augmentatoin (데이터 증강 ex. 1->7개)
- feature engineering
- domain knowledge to extract features from raw data
- applied ML
- dimensionality reduction
- Principal Component Analysis
- Independent Component Analysis
- Non-negative Matrix
- Factorization
- Uppropagation
- fix underfitting



댓글남기기